Hurricane Beryl’s Path and Intensity
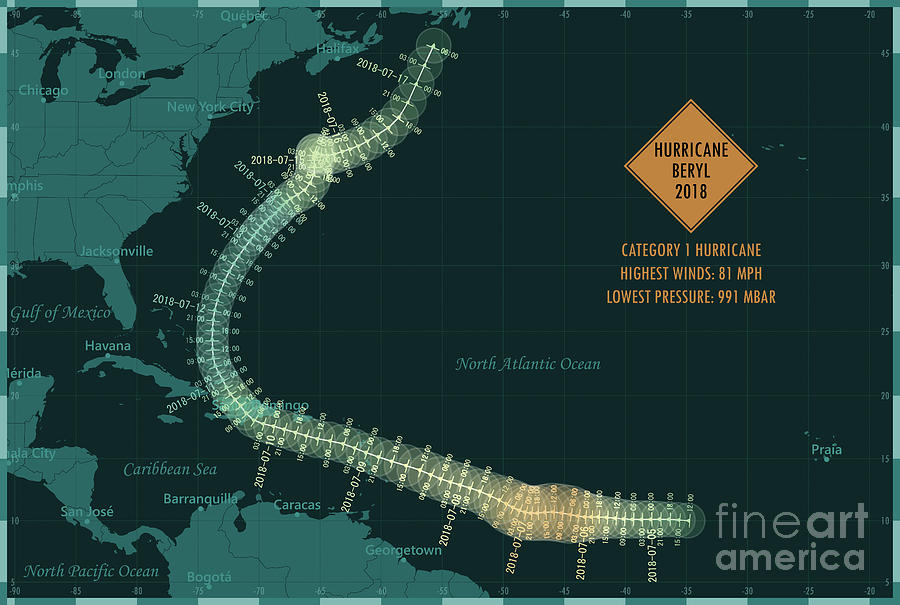
Hurricane Beryl originated as a tropical wave near the west coast of Africa on July 5, 2018. It moved westward across the Atlantic Ocean, gradually intensifying as it encountered warm ocean waters and favorable atmospheric conditions. On July 9, Beryl strengthened into a hurricane, with maximum sustained winds reaching 75 mph. The hurricane continued on a west-northwestward track, passing just north of the Leeward Islands on July 11. Beryl made landfall on the island of Dominica on July 12, bringing heavy rainfall and strong winds. It then continued across the Caribbean Sea, making a second landfall on the island of Puerto Rico on July 13.
Beryl’s path and intensity were influenced by several factors, including:
* Wind patterns: The hurricane’s westward movement was steered by the prevailing easterly trade winds.
* Ocean temperatures: The warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean provided the energy necessary for Beryl to intensify.
* Atmospheric conditions: Favorable atmospheric conditions, such as low wind shear and high humidity, allowed Beryl to maintain its strength.
Impact of Hurricane Beryl
Beryl hurricane track – Hurricane Beryl brought significant impact to the affected areas, causing widespread damage to infrastructure, property, and the environment.
The hurricane’s strong winds and heavy rainfall led to downed trees, power lines, and damaged buildings. In some areas, the flooding caused by the storm surge and heavy rains resulted in widespread property damage and displacement of residents.
Infrastructure Damage
- Downed power lines and damaged electrical infrastructure led to widespread power outages, affecting thousands of homes and businesses.
- Flooding caused damage to roads and bridges, disrupting transportation and isolating communities.
- High winds caused damage to buildings, including collapsed roofs and broken windows.
Property Damage
- Flooding inundated homes and businesses, causing extensive water damage and destroying personal belongings.
- High winds caused damage to roofs, siding, and other exterior structures.
- Debris from downed trees and other objects caused damage to vehicles and property.
Environmental Impact
- Flooding and storm surge caused erosion of beaches and coastal areas.
- High winds and heavy rainfall led to the uprooting of trees and damage to vegetation.
- The storm surge also caused saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources, affecting water quality.
To mitigate the effects of Hurricane Beryl, local authorities implemented emergency response plans, including evacuations, road closures, and the deployment of emergency personnel. Utility companies worked to restore power and repair damaged infrastructure. Residents and businesses took measures to protect their property, such as boarding up windows and securing loose objects.
Historical Context of Hurricane Beryl: Beryl Hurricane Track
Hurricane Beryl, despite its relatively short duration and limited impact, provides valuable insights into the historical context of hurricanes in the region. By comparing it to other notable hurricanes, we can draw parallels and identify patterns that inform our understanding of hurricane behavior and preparedness.
In terms of its track, Beryl shares similarities with Hurricane Irma (2017) and Hurricane Maria (2017), both of which originated in the tropical Atlantic and followed a westward path towards the Caribbean. However, Beryl’s track was more northerly than Irma and Maria, resulting in a different impact zone.
Intensity and Impact, Beryl hurricane track
In terms of intensity, Beryl reached Category 3 status, making it comparable to Hurricane Ivan (2004) and Hurricane Matthew (2016). However, Beryl’s impact was less severe than these major hurricanes, causing limited damage and no fatalities.
Lessons Learned
The experience of Hurricane Beryl has reinforced the importance of early warning systems and evacuation protocols. The timely issuance of hurricane watches and warnings allowed residents to prepare and evacuate affected areas, minimizing the potential for casualties.
Furthermore, Beryl’s relatively mild impact has highlighted the need for continued investment in hurricane preparedness and mitigation measures. By strengthening infrastructure, improving building codes, and educating communities about hurricane safety, we can reduce the vulnerability of coastal areas to future storms.
The Beryl hurricane track has been closely monitored as it churns through the Atlantic. For the latest updates on its projected path, including where it is headed, visit where is hurricane beryl headed. The hurricane’s trajectory is expected to shift in the coming days, so stay informed with the most up-to-date information on the Beryl hurricane track.
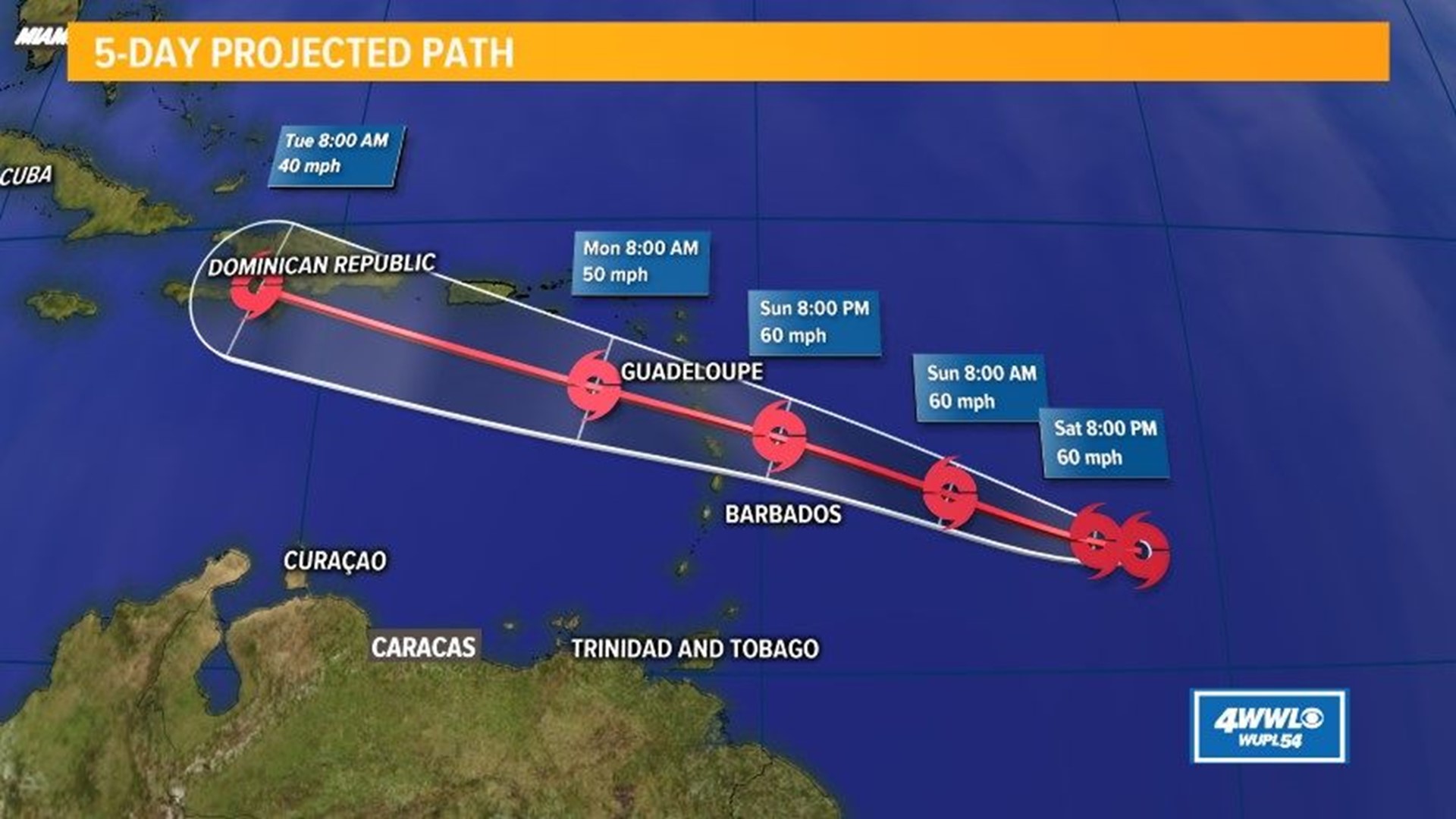
The Beryl hurricane has been closely tracked by meteorologists as it makes its way across the Atlantic Ocean. The storm is expected to weaken as it approaches the Lesser Antilles, but it is still a threat to the region. The hurricane is expected to pass near Barbados, and residents there should be prepared for possible flooding and power outages.
You can find more information about the hurricane’s potential impact on Barbados at hurricane beryl barbados. The storm is expected to continue moving west-northwest after passing Barbados, and it could still pose a threat to other islands in the Caribbean.